15 KiB
About
GitHub Action to login against a Docker registry.
💡 See also:
- setup-buildx action
- setup-qemu action
- build-push action
- Usage
- Docker Hub
- GitHub Packages Docker Registry
- GitHub Container Registry
- GitLab
- Azure Container Registry (ACR)
- Google Container Registry (GCR)
- Google Artifact Registry (GAR)
- AWS Elastic Container Registry (ECR)
- AWS Public Elastic Container Registry (ECR)
- OCI Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Registry (OCIR)
- Quay.io
- Customizing
- Keep up-to-date with GitHub Dependabot
- Limitation
Usage
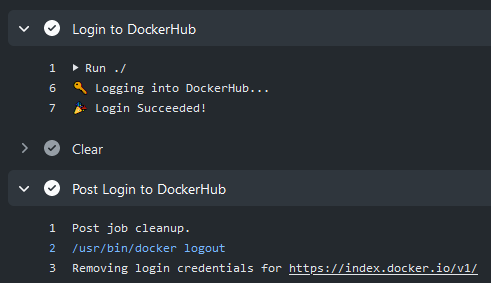
Docker Hub
To authenticate against Docker Hub it's strongly recommended to create a personal access token as an alternative to your password.
name: ci
on:
push:
branches: master
jobs:
login:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
-
name: Login to Docker Hub
uses: docker/login-action@v1
with:
username: ${{ secrets.DOCKERHUB_USERNAME }}
password: ${{ secrets.DOCKERHUB_TOKEN }}
GitHub Packages Docker Registry
⚠️ GitHub Packages Docker Registry (aka
docker.pkg.github.com) is deprecated and will sunset early next year. It's strongly advised to migrate to GitHub Container Registry instead.
You can configure the Docker client to use GitHub Packages to publish and retrieve docker images.
name: ci
on:
push:
branches: master
jobs:
login:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
-
name: Login to GitHub Packages Docker Registry
uses: docker/login-action@v1
with:
registry: docker.pkg.github.com
username: ${{ github.repository_owner }}
password: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
GitHub Container Registry
To use the GitHub Container Registry, you need to enable this feature for your personal or organization account.
To authenticate against it,
use the GITHUB_TOKEN for the best
security and experience.
name: ci
on:
push:
branches: master
jobs:
login:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
-
name: Login to GitHub Container Registry
uses: docker/login-action@v1
with:
registry: ghcr.io
username: ${{ github.repository_owner }}
password: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
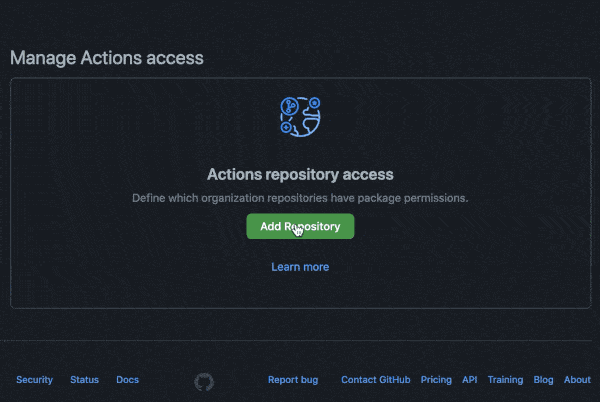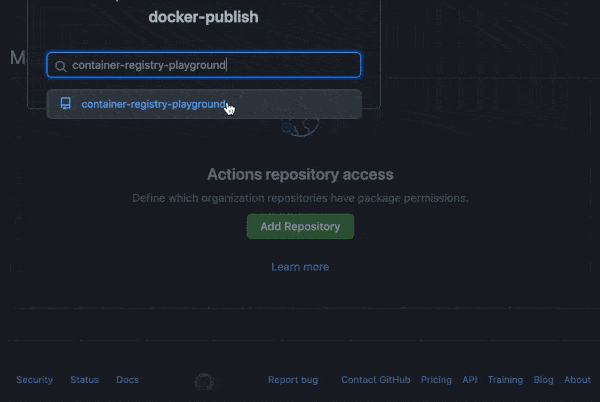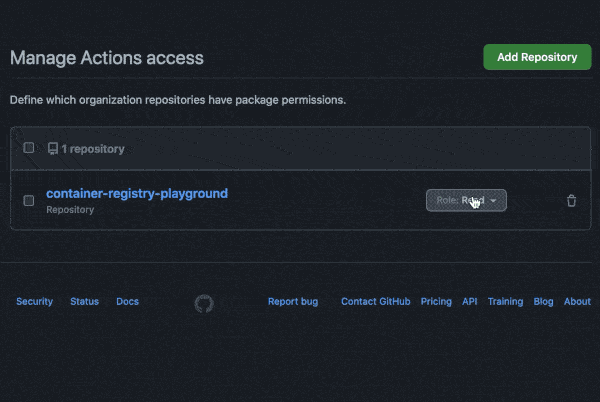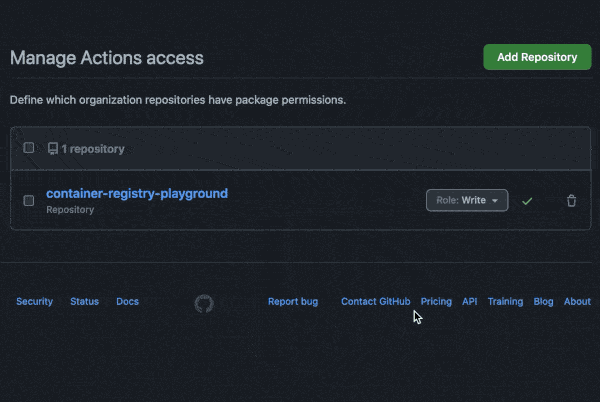
You may need to manage write and read access of GitHub Actions for repositories in the container settings:
You can also use a personal access token (PAT) with the appropriate scopes.
GitLab
name: ci
on:
push:
branches: master
jobs:
login:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
-
name: Login to GitLab
uses: docker/login-action@v1
with:
registry: registry.gitlab.com
username: ${{ secrets.GITLAB_USERNAME }}
password: ${{ secrets.GITLAB_PASSWORD }}
Azure Container Registry (ACR)
Create a service principal with access to your container registry through the Azure CLI and take note of the generated service principal's ID (also called client ID) and password (also called client secret).
name: ci
on:
push:
branches: master
jobs:
login:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
-
name: Login to ACR
uses: docker/login-action@v1
with:
registry: <registry-name>.azurecr.io
username: ${{ secrets.AZURE_CLIENT_ID }}
password: ${{ secrets.AZURE_CLIENT_SECRET }}
Replace
<registry-name>with the name of your registry.
Google Container Registry (GCR)
Google Artifact Registry is the evolution of Google Container Registry. As a fully-managed service with support for both container images and non-container artifacts. If you currently use Google Container Registry, use the information on this page to learn about transitioning to Google Artifact Registry.
Use a service account with the ability to push to GCR and configure access control.
Then create and download the JSON key for this service account and save content of .json file
as a secret
called GCR_JSON_KEY in your GitHub repo. Ensure you set the username to _json_key.
name: ci
on:
push:
branches: master
jobs:
login:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
-
name: Login to GCR
uses: docker/login-action@v1
with:
registry: gcr.io
username: _json_key
password: ${{ secrets.GCR_JSON_KEY }}
Google Artifact Registry (GAR)
Use a service account with the ability to push to GAR and configure access control.
Then create and download the JSON key for this service account and save content of .json file
as a secret
called GAR_JSON_KEY in your GitHub repo. Ensure you set the username to _json_key.
name: ci
on:
push:
branches: master
jobs:
login:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
-
name: Login to GAR
uses: docker/login-action@v1
with:
registry: <location>-docker.pkg.dev
username: _json_key
password: ${{ secrets.GAR_JSON_KEY }}
Replace
<location>with the regional or multi-regional location of the repository where the image is stored.
AWS Elastic Container Registry (ECR)
Use an IAM user with the ability to push to ECR with AmazonEC2ContainerRegistryPowerUser managed policy for example.
Then create and download access keys and save AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID and AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY as secrets
in your GitHub repo.
name: ci
on:
push:
branches: master
jobs:
login:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
-
name: Login to ECR
uses: docker/login-action@v1
with:
registry: <aws-account-number>.dkr.ecr.<region>.amazonaws.com
username: ${{ secrets.AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID }}
password: ${{ secrets.AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY }}
If you need to log in to Amazon ECR registries associated with other accounts, you can use the AWS_ACCOUNT_IDS
environment variable:
name: ci
on:
push:
branches: master
jobs:
login:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
-
name: Login to ECR
uses: docker/login-action@v1
with:
registry: <aws-account-number>.dkr.ecr.<region>.amazonaws.com
username: ${{ secrets.AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID }}
password: ${{ secrets.AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY }}
env:
AWS_ACCOUNT_IDS: 012345678910,023456789012
Only available with AWS CLI version 1
You can also use the Configure AWS Credentials action in combination with this action:
name: ci
on:
push:
branches: master
jobs:
login:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
-
name: Configure AWS Credentials
uses: aws-actions/configure-aws-credentials@v1
with:
aws-access-key-id: ${{ secrets.AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID }}
aws-secret-access-key: ${{ secrets.AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY }}
aws-region: <region>
-
name: Login to ECR
uses: docker/login-action@v1
with:
registry: <aws-account-number>.dkr.ecr.<region>.amazonaws.com
Replace
<aws-account-number>and<region>with their respective values.
AWS Public Elastic Container Registry (ECR)
Use an IAM user with the ability to push to ECR Public with AmazonElasticContainerRegistryPublicPowerUser managed policy for example.
Then create and download access keys and save AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID and AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY as secrets
in your GitHub repo.
name: ci
on:
push:
branches: master
jobs:
login:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
-
name: Login to Public ECR
uses: docker/login-action@v1
with:
registry: public.ecr.aws
username: ${{ secrets.AWS_ACCESS_KEY_ID }}
password: ${{ secrets.AWS_SECRET_ACCESS_KEY }}
env:
AWS_REGION: <region>
Replace
<region>with its respective value (defaultus-east-1).
OCI Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Registry (OCIR)
To push into OCIR in specific tenancy the username
must be placed in format <tenancy>/<username> (in case of federated tenancy use the format
<tenancy-namespace>/oracleidentitycloudservice/<username>).
For password create an auth token. Save username and token as a secrets in your GitHub repo.
name: ci
on:
push:
branches: master
jobs:
login:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
-
name: Login to OCIR
uses: docker/login-action@v1
with:
registry: <region>.ocir.io
username: ${{ secrets.OCI_USERNAME }}
password: ${{ secrets.OCI_TOKEN }}
Replace
<region>with their respective values from availability regions
Quay.io
Use a Robot account with the ability to push to a public/private Quay.io repository.
name: ci
on:
push:
branches: master
jobs:
login:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
-
name: Login to Quay.io
uses: docker/login-action@v1
with:
registry: quay.io
username: ${{ secrets.QUAY_USERNAME }}
password: ${{ secrets.QUAY_ROBOT_TOKEN }}
Customizing
inputs
Following inputs can be used as step.with keys
| Name | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
registry |
String | Server address of Docker registry. If not set then will default to Docker Hub | |
username |
String | Username used to log against the Docker registry | |
password |
String | Password or personal access token used to log against the Docker registry | |
logout |
Bool | true |
Log out from the Docker registry at the end of a job |
Keep up-to-date with GitHub Dependabot
Since Dependabot
has native GitHub Actions support,
to enable it on your GitHub repo all you need to do is add the .github/dependabot.yml file:
version: 2
updates:
# Maintain dependencies for GitHub Actions
- package-ecosystem: "github-actions"
directory: "/"
schedule:
interval: "daily"
Limitation
This action is only available for Linux virtual environments.